Jul 25 2022Reviewed by Alex Smith
当今的大多数存储系统(ESS)已经开始使用锂离子电池(LIBS),在辅助电池中技术成熟最高。
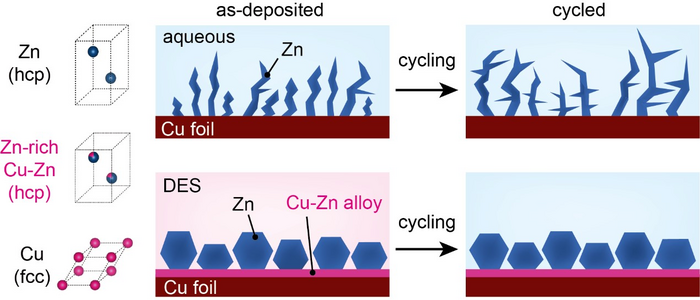 Unlike zinc particles, which are irregularly formed in a conventional aqueous electrolyte and induce corrosion, zinc grown in a DES solution is tight and uniform and maintains a stable structure even after charging and discharging in an aqueous electrolyte. Image Credit: Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST)
Unlike zinc particles, which are irregularly formed in a conventional aqueous electrolyte and induce corrosion, zinc grown in a DES solution is tight and uniform and maintains a stable structure even after charging and discharging in an aqueous electrolyte. Image Credit: Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST)
However, it is argued that due to the risk of fire, these are inappropriate for ESSs, which store significant amounts of electricity. The unpredictability of the international supply of raw materials to build LIBs has also become a critical concern.
On the other hand, aqueous zinc-ion batteries (AZIBs) tend to utilize water as the electrolyte, which essentially prevents battery ignition. Moreover, the cost of zinc, the raw material, is just one-sixteenth of that of lithium.
该研究小组由Minah Lee博士在储能研究中心领导韩国科学技术学院亚博老虎机网登录(Kist; Seok-Jin Yoon总统)报告说,他们已经成功地提出了一项制造所谓的“高密度锌金属阳极”的技术,这是对阿齐布斯商业化的主要产品。
预计这种制造技术可以作为巨大生产Azibs的催化剂,因为锌金属阳极以及高能量密度和寿命长,可以通过轻松的电镀过程来通过使用环境友好型和负担得起的解决方案来产生。
从理论上讲,由于Azibs倾向于每个离子使用两个电子,因此与碱金属离子电池相比,它们对体积能密度有益。如果锌金属的能力用作制造电池的阳极的能力不会超过两倍的阴极,则可以理解与目前商业化的LIB相似的能量密度。
Additionally, even if the zinc metal’s capacity is five times greater than that of the cathode, it is still competitive because it is comparable to sodium-ion batteries, which are garnering interest as the next generation of batteries due to their low price and abundant supply of raw materials.
But zinc metal anodes tend to limit the energy density and lifespan of AZIBs due to the uneven growth of nanoparticles at the time of the battery operation.
在阳极中,低锌金属颗粒密度和较大的表面积与电解质加速腐蚀,从而排干电解质和活性锌金属。
Current studies normally utilized zinc metals that were nearly 20 times thicker compared to what was needed to neutralize the lifespan limitations; paradoxically, this resulted in an unavoidable decline in energy density and price competitiveness, the highest strengths of AZIBs.
The team headed by Dr. Minah Lee at KIST regulated the microstructure of zinc metal anodes to decrease the prevalence of the side reactions that induce the drop in energy density and also the lifespan of AZIBs.
研究小组已经采用了深层溶剂(DES)溶液,该溶液可以在室温下轻松合成以构建紧凑的锌阳极。该溶液由氯化胆碱和尿素制成,以1:2的摩尔比混合。混合物变成液体复合物,熔点为12°C。
科学家证实,锌酚锌合金层在DES内的铜和锌电流收集器之间自由发展。这使高密度的锌颗粒得以生长。yabo214
科学家们成功地利用了这一突破来提出一个电镀工艺,该过程使锌金属能够在环保且负担得起的DES解决方案中以密集甚至方式生长。
制成的锌金属阳极在水性锌电池系统中的应用表明,腐蚀反应被有效抑制。同样,在重复7000多个费用后,该容量已保留在70%以上。
与使用薄锌的类似研究相比,这种结果是不寻常的,并且远远超过了充电和放电寿命(1000到2000次)的价值。
我们能够开发一种核心技术,用于商业化可以解决ESS的消防安全问题的Azibs,这是提供和扩展可再生能源的最大障碍。
韩国科学技术研究所Minah Lee博士亚博老虎机网登录
李补充说:“We expect that this compact zinc anode manufacturing technology will open the way for the mass production of AZIBs by combining a particularly economical and eco-friendly DES solution with an electroplating process already widely used throughout the industry。”
Journal Reference:
M. Kwon,,等。(2022) Stimulating Cu–Zn alloying for compact Zn metal growth towards high energy aqueous batteries and hybrid supercapacitors.Energy & Environmental Science。doi.org/10.1039/D2EE00617K。
来源:https://eng.kist.re.kr/