The RF focusing fields in the Vocus ion molecule reactor improve sensitivity while maintaining product ion energies and recorded branching ratios that are nearly identical to those of traditional drift-tube PTR ion-molecule reactor designs.

Felipe Lopez-Hilfiker, Liang Zhu, Manuel Hutterli, Carsten Stoermer,
Luca Cappellin
托夫沃克,瑞士杜恩
质子转移反应质谱仪(PTR-MS)的灵敏度的提高主要源于质量分析仪的升级和将PTR离子 - 分子反应器(IMR)与质量分析仪相对的离子转移阶段的改善。直到最近,人们的注意力转向了PTR IMR的设计,PTR IMR在过去十年中基本上没有变化。
Traditional PTR IMRs – often called drift-tube IMRs – consist of stacked ring electrodes connected by a resistor network to generate a linear electrostatic field. In combination with the precisely controlled IMR pressure and temperature, this electric field defines ion-molecule collision energies, reactant ion distributions and reaction times. The collision conditions in drift tube IMRs can be calculated from first principles, making it straightforward to predict the energy and fragmentation of product ions. But, >90% of product ions are lost in the IMR due to diffusion and scattering, significantly limiting instrument sensitivity.
Tofwerk vocus离子分子反应堆1开发以克服这些类型的离子损失。振荡射频(RF)字段叠加在线性漂移场上,以增加IMR的离子传输,从而提高PTR-MS敏感性。在使用RF场的任何离子引导装置中,离子所经历的瞬时电场取决于其质量和与RF电极的距离。与漂流管IMR相反,这种增加的复杂性使得很难计算净碰撞条件,如果不正确的设计或使用,则可能导致定量和高片段化比率的潜在错误。本说明回顾了VOCUS IMR的设计,讨论了IMR中离子所经历的电场,并将标准操作条件下的碰撞能和碎片模式与漂移管IMR的碰撞和碎片模式进行了比较。
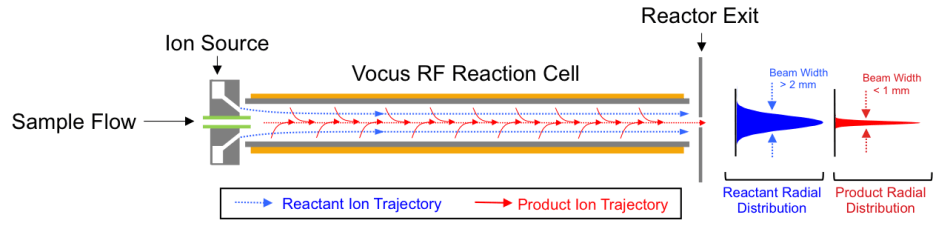
Figure 1 Schematic of Vocus IMR showing ion trajectories for both reactant ions and product ions (greater than 50 Th).The resistive-glass reaction cell (grey) is housed inside the four rods of an rf-only quadrupole (orange). Low mass-to-charge reactant ions (19 Th, blue) reactant ions are not as tightly focused as higher mass-to-charge product ions (red), which are rapidly focused to the central axis by the applied RF field.
VOCUS反应器将RF聚焦在轴向漂移场上
图1中示意性地显示的Tofwerk vocus离子分子反应器由一个电阻式玻璃管反应细胞(灰色)组成,该反应细胞(灰色)包含在四极离子导向器中(黄色)。IMR的上游,水蒸气通过低压等离子体来产生H3O+反应物离子高丰富。这些离子通过淬火区域进入IMR,以确保高反应物离子纯度。2采样空气通过位于反应器轴上的毛细管进入IMR。从H3O转移质子+在通过细胞的〜100 µs转运过程中,反应物离子对中性分析物分子形成产物离子。传统的轴向静电场遍布玻璃管的长度,以控制反应时间和碰撞条件。RF场与该轴向DC场的叠加将产物离子聚焦于狭窄的光束中,以有效地通过出口孔口传递。
VOCUS IMR中的产品离子迅速集中,并受到有限的加热
The RF field strength experienced by ions in the Vocus IMR depends on their radial positions relative to the central axis of the glass reaction cell. The larger the distance of an ion from center, the more energy it gains from the RF. Such heating of unfocused ions could potentially drive fragmentation or complicate the ion chemistry. As depicted in Figure 1, though, the quadrupole field used in the Vocus IMR rapidly focuses product ions close to the central axis where the net RF field strength is 0V.
这在图2中证明了这一点,该图显示了在2 MBAR操作的VOCUS反应器中质量/电荷的径向分布,以及相应的轴向和径向动力学能量,如Simion建模。轴向能(红色)由IMR两端之间的直流电场驱动,并且对径向位置几乎没有依赖。由RF场驱动的径向能(黑色)在中心轴上为零,并且随着离子从中心移动而迅速上升。RF场的聚焦产生的产品离子(蓝色)的紧密空间分布,大多数离子限制在中心轴附近,因此由于RF而获得的能量受到限制,因此与常规漂移管相比,碰撞条件在很大程度上没有变化PTR反应堆。
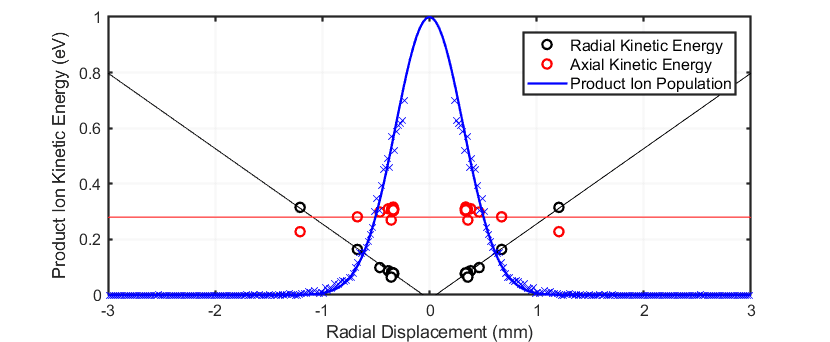
Figure 2 (blue) Radial distribution of product ions with mass/charge of 100 Th in a Vocus reactor operated at 2 mbar and (black) radial and (red) axial components of ions’ kinetic energies as modeled by SIMION.由RF场驱动的能量的径向分量在中央轴上为零,并且随着径向位移的形式增加。轴向动能是由沿反应器轴施加的直流场驱动的,对径向位置几乎没有依赖。RF场迅速将产品离子聚焦到中心轴,因此由于施加的RF引起的净加热非常有限,并且总体动能与仅DC漂移场仅经历的相似。
RF聚焦可提高灵敏度而不增加碎片
α-Pinene (C10H16)经常使用传统漂移管离子分子反应器测量PTR-MS3并已知具有一个主要的片段产物离子(C6H9+)。该片段和分子离子的相对强度(c10H16H+) depend strongly on the net collision conditions in the reaction cell. Measurement of these intensities can be used to characterize the net heating in the Vocus IMR and to compare the Vocus to traditional systems.
图3显示了扫描VOCUS RF振幅(以固定频率)对α-pine烯分支比率的影响,并在典型的IMR工作压力和升高的IMR工作压力下观察到灵敏度。左上图显示了与漂移管IMR3的文献值相比,在2 MBAR处记录的分支比(显示为幅度= 0V的实心点)。如图2所示,RF场在此压力下迅速将离子聚焦到中心轴。由于径向加热在中心附近可以忽略不计,因此有效的离子温度不会随RF振幅的函数而变化,并且即使在高幅度下,分支比也接近已发布的漂移管值。同时,与仅具有轴向漂移场的操作相比,RF的增加改善了IMR的聚焦和传输,敏感性提高了> 10 x。
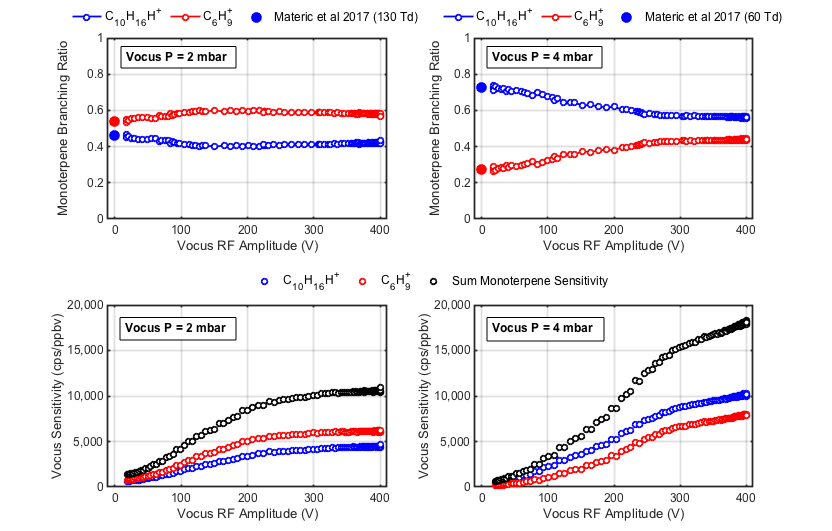
图3在VOCUS IMR中,应用的RF振幅对观察到的(顶)碎片和(底部)敏感性(左)标准和(右)升高工作压力的影响。上图中的填充点显示了在这些压力下的传统漂移管的分支比的公布值。在低压下,RF有效地沿着径向加热接近零的中心轴有效聚焦了产物离子束,并且即使在高RF下,也以“漂移管极限”的反应器传递产物离子。在较高的压力下,数据显示的总体碎裂较少,因为离子分子碰撞的能量较低。RF场在将产品离子聚焦到中心轴上的效率较低,并且随着RF的增加,碎片化略有增加。在两种压力下使用的RF使用RF的绝对灵敏度增加了一个数量级,从而提高了测量质量和速度。
The panels on the right display the same data recorded at a Vocus IMR pressure of 4 mbar. Overall sensitivity increases with the increase in pressure because ion-neutral collisions become more frequent. Collisions also become less energetic, leading to less fragmentation compared to the lower pressure operation. With no applied RF, the spectrum is dominated by the molecular ion and consistent with the published value. Focusing by the RF field is less effective at this pressure and product ions are – on average – farther from the central axis than in the 2-mbar case. Because more ions are in the region where radial heating is significant, the increase in RF does increase the observed degree of fragmentation (although the molecular ion does remain dominant even at high RF). Similar to the 2 mbar experiment, the addition of the RF fields leads to a substantial improvement in sensitivity.
结论
VOCUS离子分子反应器唯一使用RF聚焦场来克服PTR-MS中常规漂移管反应器的典型扩散离子损耗。这种聚焦增加了灵敏度超过10倍。在典型的工作压力(〜2 MBAR)下,沿Vocus反应器的中央轴迅速聚焦的产物离子,该离子不会从施加的RF磁场中经历额外的加热。在此制度中,产物离子能和记录的分支比与传统漂移管离子分子反应器设计的记录几乎相同。
参考
- Krechmer,J。;Lopez-Hilfiker,F。;等人,评估新的VOCUS试剂源和聚焦离子 - 分子反应器,用于用于质子转移反应质谱法。肛门。Chem。,2018。90(20),12011。10.1021/acs.analchem.8B02641
- 高纯度H3O+反应物离子可以简单解释VOCUS PTR-TOF数据,白皮书,Tofwerk,2019,2019,https://www.tofwerk.com/vocus-high-purity-reactant-ions/
- Materić D; et al., Monoterpene separation by coupling proton transfer reaction time-of-flight mass spectrometry with fastGC. Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2015, 407 (25), 7757.10.1007/S00216-015-8942-5
来源:https://www.tofwerk.com/