There has been a significant interest in and investigation into the effects of introducing carbon-fluorine bonds into organic compounds. This process can substantially affect organic compounds’ physical and chemical properties, particularly when compared to their non-fluorinated analogs.1

图片信条:Analytik Jena US
Most of the critical products in the chemical and life-science sectors depend on organic fluorine chemistry for their functional and beneficial properties, including pharmaceuticals, polymers and both fine and specialty chemicals.
Fluorinated organic substances are being produced in increasingly large volumes, resulting in their increasing release into the environment, with both the Stockholm Convention (Annex B-restriction) and the European water framework directive (WFD) already listing these substances as persistent organic pollutants.
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) represent a wide-ranging class of synthetic chemicals that present a range of analytical challenges, including their widespread presence in environmental samples.2
PFA有可能污染为美国估计有1900万人服务的公共饮用水系统,促使美国环境保护署(EPA)实施一项强大而紧急的PFAS行动计划,这是最详细且最深远的跨界行动计划代理计划迄今为止旨在解决新兴的关注化学化学物质。2,3
EPA在饮用水中建立了不可执行的健康咨询水平,为饮用水中的70(PPT),五氟氯辛酸(PFOA)和甲氟二氟辛烷磺酸(PFOS)的总量。
在整个2021年,EPA一直在努力开发快速筛选工具,能够识别PFAS的总存在和不存在。即将到来的标准操作程序(SOP)适合量化总有机氟(TOF).4
This has necessitated the development of a sensitive, rapid and straightforward TOF detection method suitable for monitoring and managing environmental pollution.
This method makes use of solid-phase extraction (SPE) and high-resolution–continuum source graphite furnace molecular absorption spectrometry (HR-CS GF MAS).
The solid phase extraction (SPE) procedure has been fully discussed in other studies, detailing its potential for the extraction of fluorinated compounds. These studies saw HR-CS GF MAS employed in the detection of total fluorine via in-situ formation of gallium(I) fluoride (GaF) molecules.
此处介绍的研究旨在通过使用新颖的校准策略和HR-CS GF MAS方法的组合来增强废水中总植物(TF)分析的性能。
Method Development Strategy
有必要为HR-CS GF MAS开发和优化物种不合别的响应,以使氟化有机化合物作为总参数进行定量。
Previous research had highlighted the suitability of gallium in enabling the most sensitive fluorine detection via diatomic GaF formation. GaF’s characteristic molecular absorption can be detected via HR-CS GF MAS.
在样品注入之前,将炉管与分子成型剂(GA)和修饰符(PD/mg/ZR/BA)进行调节,以实现最佳信号。
Existing literature confirms that the melting point and vapor pressure of fluorinated compounds can have a considerable effect on different compounds’ recovery rates. To account for this, the furnace program’s drying and pyrolysis procedures were optimized to help minimize the potential losses of fluorinated compounds.
To enable the effective evaluation of the optimization approach, a total of 24 different fluorine compounds were mixed to act as a QC sample. These 24 compounds were selected to include varying numbers of fluorine atoms and boiling points.
Using this QC sample, it was possible to develop calibration strategies to obtain the best recovery rate.
Materials and Methods
试剂
- 超纯级HNO3
- 0。05% TritonX-100
- Pd/Mg/Zr modifier (1 g/L Pd, 0.5 g/L Mg, 0.02 g/L Zr)
- BA修饰符(10 mg/L)
- Ga solution (10 g/L)
- ZR库存解决方案(1 g/l)
- 认证的F股票解决方案(0.1 g/l f icp标准为NAF)
- 七氟二氟辛磺酸溶液(PFOS,100μg/ml甲醇,分析标准)
- Pentadecafluorooctanoic acid solution (PFOA, 100 μg/mL in methanol, analytical standard)
Samples
- QC样品:24种氟化有机化合物混合物(TOF约128 µg/L)
- 废水sample
仪器
AcontrAA®800克石墨炉AAS在整个研究中,使用AS-GF自动采样器。这是使用CS软件进行控制的,从而确定了氟。
Prior to use, the graphite tube was coated six times with zirconium (35 µL stock solution). It was then possible to determine fluorine content by measuring the intensity of the gallium monofluoride absorption band.
Fluorine is converted stoichiometrically to GaF in the presence of gallium throughout the analysis process. A conditioning procedure was included in the furnace program to improve sensitivity, and each individual sample was analyzed with three replicates.
表2和表3提供了方法设置和熔炉程序的详细信息。
Table 1.Instrument specifications. Source: Analytik Jena US
| 范围 |
Specification |
| Instrument |
Contraa 800 g |
| Furnace tube type |
PIN platform |
| Autosampler |
AS-GF |
| 注射体积 |
4-20 µL(标准),20 µL(样品) |
| rinsing solution |
2%HNO3, 0.05% TritonX-100 |
Table 2.方法设置和评估参数。资料来源:Analytik Jena我们
| 分子 |
Wave-length [nm] |
No. of eval. pixels |
t pyr。[°C] |
T Atomis. [°C] |
ramp [°C/s] |
Meas. Time [s] |
Modifier |
基线校正 |
| GAF |
211。248 |
5 |
500 |
1450 |
1200 |
5 |
5µL Pd/Mg/Zr modifier*
5µl Ga solution*
3 µL GA溶液
5µl Ba solution |
IBC |
注意: * - 在条件步骤中使用
表3。用于检测GAF分子的炉程序。资料来源:Analytik Jena我们
| Step |
姓名 |
Temp (°C) |
ramp (°C/s) |
持有 |
Gas purge |
| 1 |
烘干* |
80 |
6 |
5 |
max |
| 2 |
Drying |
100 |
6 |
5 |
max |
| 3 |
Drying |
160 |
10 |
5 |
max |
| 4 |
Drying |
350 |
25 |
10 |
max |
| 5 |
Drying |
1100 |
500 |
12 |
max |
| 6 |
Drying |
70 |
NP |
10 |
max |
| 7 |
干燥^ |
80 |
2 |
10 |
max |
| 8 |
Drying |
110 |
5 |
15 |
max |
| 9 |
Pyrolysis |
250 |
50 |
5 |
max |
| 10 |
Pyrolysis |
500 |
200 |
5 |
max |
| 11 |
Gas adaption |
500 |
0 |
5 |
停止 |
| 12 |
Atomization |
1450 |
1200 |
5 |
停止 |
| 13 |
Clean |
2450 |
1200 |
4 |
max |
Note: *-modifier injection for pretreatment, ^-sample injection
校准策略
氟化化合物的熔点和蒸气压在总氟的分析中起重要作用。
如果在各个物质的给定温度下的蒸气压很高,则可以将分析物转移到气相中,并通过炉程序的氩气流传输,然后才能检测和分析。
为了减轻这种风险,重要的是要选择校准标准,以确保这些行为与样品本身相似。因此,准备三个不同的校准集准备为废水找到最佳的校准策略(表4)。
表4。浓度集。资料来源:Analytik Jena我们
| 校准集 |
F Compounds |
ratio |
| Inorganic F |
NAF |
|
| 有机f |
PFOS, PFOA, HFPO-DA |
1:1:1 |
| 无机和有机F混合物 |
NAF, PFOS, PFOA, HFPO-DA |
1:1:1:1 |
使用1000 ppm的NAF储备溶液来制备无机氟化物校准(无机F)的校准标准。
Atotal of three frequently encountered fluorinated compounds - PFOS, PFOA and HFPO-DA - were used to generate organic fluorine (organic F) standards, while the inorganic and organic mixture standard was generated using NaF, PFOS, PFOA and HFPO-DA.
表5显示了标准的浓度,吸光度和校准的整体线性。校准曲线和测量的空白值表明,可以使用无机和有机混合物校准实现最低的LOD(4.00 µg/L)。
无机氟化物校准标准表现出最高的信号,而有机校准标准显示最低(表5)。确定有机和无机物质的热稳定性影响了它们不同的信号反应。
表5。Type and quality of calibration. Source: Analytik Jena US
| 姓名 |
浓 |
Inorganic F |
有机f |
无机和有机混合物 |
| Unit |
µg/L |
腹肌 |
腹肌 |
腹肌 |
| Cal-Zero1 |
0 |
0。1726 |
0。1153 |
0。1709 |
| Cal-Std1 |
125 |
1。6650 |
0。5177 |
1.1601 |
| Cal-Std2 |
250 |
3.0402 |
1。0367 |
1.7833 |
| Cal-Std3 |
375 |
4。4542 |
1。4847 |
2。4628 |
| Cal-Std4 |
500 |
5。9955 |
1.9403 |
3。0694 |
| r2 |
|
0。9993 |
0。9999 |
0。9808 |
| LOD (µg/L) |
|
7.74 |
12。58 |
4。00 |
Anumber of volatile PFAS are lost to a degree throughout the furnace program’s drying and pyrolysis steps, but inorganic fluoride remains thermally stable during this process.
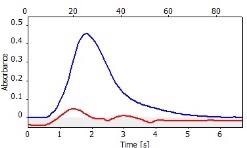
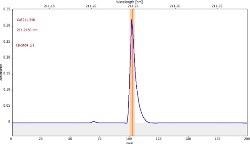
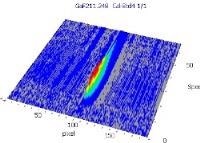
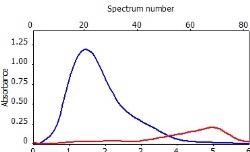
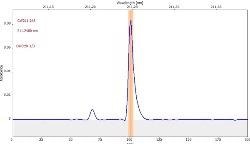
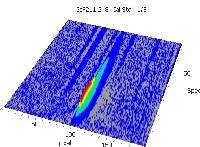
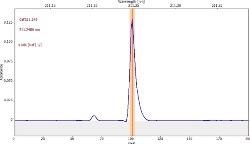
表6显示了与三个校准集的211.248 nm处的清晰,无干扰的GAF吸光度光谱(蓝色)。
表6。分析物线的特征信号形状和光谱附近。资料来源:Analytik Jena我们
| Element |
信号剖面* |
Spectral vicinity |
3D光谱 |
| Inorganic F Cal 4 |
 |
 |
 |
| 有机fCal 4 |
 |
 |
 |
| 无机和有机混合物Cal 4 |
 |
 |
 |
*-blue: GaF analyte signal, red: background signal
results and Discussion
Inorganic F Calibration Strategy Results
The QC standard of24种氟有机化合物在整个无机F校准策略中显示了38%的回收率(表7)。
Variations in signal response result in low PFAS recovery rates when employing NaF solutions as the calibration standard. The QC sample demonstrates a good spike recovery rate of 114% when spiked with 100 µg/L F (as NaF).
Table 7.Measurement results by inorganic F calibration. Source: Analytik Jena US
| Samples |
浓(µg/l) |
recovery (%) |
| Blank water |
|
|
| QC sample |
48。9 |
38 |
| QC样品用100 µg/L(NAF)加标 |
162.5 |
114 |
| 废水 |
348。2 |
|
有机F校准策略结果
The QC sample’s recovery is 190% with the organic F calibration strategy. This overestimation of PFAS is the result of the varying thermal stabilities of the different organic fluorinated compounds.
Spiking the QC with 100 µg/L NaF yielded a 275% spike recovery rate due to the more robust stability and the improved signal response of NaF.
The QC and wastewater samples were both spiked with 125 µg/L F from the TOF mixture; a mixture made up of the same compounds as the organic calibration standards. Spike recovery rates for both the QC and wastewater were found to be 74%.
Table 8.通过有机F校准测量结果。资料来源:Analytik Jena我们
| Samples |
浓(µg/l) |
recovery (%) |
| Blank water |
|
|
| QC sample |
224.7 |
174 |
| QC样品用125 µg/l F(TOF*)加标本 |
316。7 |
74 |
| QC sample spiked with 100 µg/L F (NaF) |
628.1 |
275 |
| 废水 |
4882。5 |
|
| 废水(1:50 dilution) spiked with 125 µg/L F (TOF*) |
|
74 |
*TOF = PFOS, PFOA, HFPO-DA (ratio 1:1:1)
Inorganic and Organic Mixture Calibration Strategy Results
The organic and inorganic F mixture calibration strategy was determined to offer the best approximation of sample analyte characteristics, as illustrated in Table 9.
QC sample recovery rate was determined to be 100%. Both the QC sample and wastewater sample were spiked with 125 µg/L F from the TF mixture.
TF混合物中的化合物与无机和有机混合物校准标准中的化合物相同。
QC样品和废水样品的尖峰回收率分别为85%和86%。
QC样品还用无机F升高,由于无机NAF的热稳定性提高,恢复速率高估了167%。
在三种校准策略之间进行了比较。这突出了校准成分对分析结果的显着影响,进一步强调,无机和有机F混合物校准策略是该特定QC样本的最佳选择。
Table 9.通过无机和有机混合物校准测量结果。资料来源:Analytik Jena我们
| Samples |
浓(µg/l) |
recovery (%) |
| Blank water |
|
|
| QC sample |
127.6 |
100 |
| QC样品尖峰,具有125 µg/l F(TF*) |
252.6 |
85 |
| QC standard spike with 100 µg/L F (NaF) |
380。9 |
167 |
| 废水 |
1936。5 |
|
| 废水(1:50) spike with 125 µg/L F (TF*) |
|
86 |
*TF = NaF, PFOS, PFOA, HFPO-DA (ratio 1:1:1:1)
Long-Term Stability Test
To assess the long-term stability of this method, tests were performed on the QC sample on three separate days, each one week apart.
这三个测试利用了测试1的校准曲线,没有重新校准,在此期间,这三个测试的RSD为5.7%(表10)。这自信地确立了该方法的长期稳定性。
表10。Long-term stability test. Source: Analytik Jena US
|
浓(µg/l) |
RSD(5重复) |
| 测试1(第1周) |
127.6 |
3。8% |
| 测试2(第2周) |
113。8 |
3。0% |
| 测试3(第3周) |
120。2 |
2.7% |
| Average Conc. |
120。5 |
|
| RSD |
5.7% |
|
Blank Value
在方法优化期间观察到了相对较高的空白值。这在很大程度上是由于样本简介系统中的结转效应。
添加HNO3Tritonx-100到冲洗解决方案导致空白值较低。在整个过程中使用无F的修饰符很重要,建议使用高纯盐来制备这些修饰符,例如胆汁(III)硝酸盐水合物。
Conclusion
此处介绍的研究表明,一种快速,直接,敏感的互补方法,用于废水中的全氟分析。
该研究说明了使用MAS方法的成功应用Contraa 800 g仪器for measurements. The optimized furnace program and calibration strategy were found to provide high sample throughput, sensitivity and accuracy.
每个样品需要每次重复3.5分钟,使用无机和有机混合物校准策略达到100%的QC样品回收率。也可以使用无机和有机混合物校准策略来实现最低的LOD(4 ppb)。
通过HR-CS GF MAS测定氟的结果表现出良好的可重复性和长期稳定性。该方法不需要任何其他清洁步骤,并且证明可以使用AS-GF AutoSampler轻松实现样品稀释和尖峰。
参考
- 理查德(Richard)钱伯斯,F.R.S。;有机化学中的氟。Blackwell Publishing Ltd. 2004
- EPA新闻办公室;在EPA上积极解决PFA;https://www.epa.gov/newsreleases/aggressively- addressing-pfas-epa; 2020 Jan
- Cheryl H。:为什么在饮用水中限制PFA是美国的挑战。化学和工程师新闻。2020年7月;98(27)
- https://www.epa.gov/water-research/pfas-analytical-methods-development-and-sampling-research
- Metzger, M.; Ley, P.; Sturm, M. and Meermann, B.; SCREENING METHOD FOR EXTRACTABLE ORGANICALLY BOUND FLUORINE (EOF) IN RIVER WATER SAMPLES BY MEANS OF HIGH-RESOLUTION-CONTINUUM SOURCE GRAPHITE FURNACE MOLECULAR ABSORPTION SPECTROMETRY (HR-CS GFMAS). Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019 Jul; 411 (19): 4647-4660

此信息已从Analytik Jena US提供的材料中采购,审查和改编。亚博网站下载
For more information on this source, please visitAnalytik Jena我们。