传统的能量色散X射线光谱已在高X射线能量下运行,因为这会减少背景噪声和改进的线路分离。但是,基于半导体的技术或高级合金中的现代分析需要改进的空间分辨率。
Ultim®Range of EDS Detectors
在这些困难条件下工作时提供最佳灵敏度Ultim®EDS检测器范围使用优化的几何形状与最大的SDD结合使用,可靠地提供了提高的计数率。
To be able to analyze samples with finely detailed structures, such as the NAND Flash memory device in this article which has features of sizes between 10 – 500 nm, a high spatial resolution is required.
通过低KV EDS分析NAND闪存设备
NAND闪存样品还包含一系列覆盖X射线频谱的宽部分的不同元素。为了达到高ED分辨率,必须减少生成X射线的体积。纯铁中L系列X射线的X射线生成体积,并且随着入射电子能量从20 kV降低到1 kV,体积减小。图1。
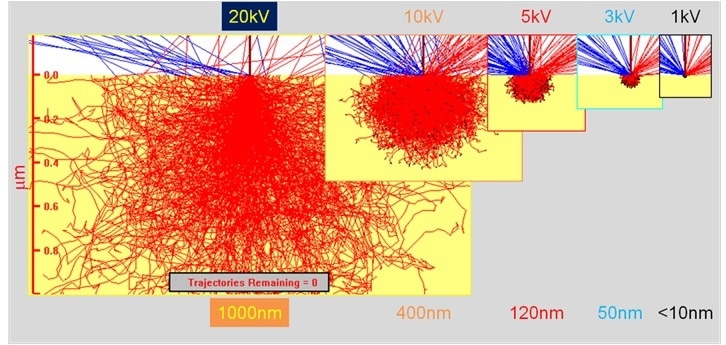
图1。在不同电子能量时,纯Fe中FeLαX射线的发电体积的蒙特卡洛模拟。
减少入射电子的能量还意味着产生X射线较少,可用的X射线线更少。例如,在相同条件下的纯铁将入射电子能量从20 kV变为10 kV,导致K系列X射线线减少90%(显着降低),而L系列无变化。将能量降低到5 kV或3 kV,导致K系列线减少100%,而L系列降低了50%或80%。
To overcome this loss in counts the sensitivity of an X-ray detector must be maximized. The sensitivity of a detector is defined by the solid angle that it subtends. Generated X-rays are emitted in a hemisphere from the surface of the specimen at the incident beam position. The solid angle of a detector is the amount of this hemisphere that it captures and can be described by dividing the area of the detector (A) by the distance between the detector and the sample squared (d2)。
固体角度〜A ⁄ D2(1)
可以通过最大化A并最小化d来增加实体角度,因此可以增加收集的计数数量。当以非常低的电子能量(给出非常低计数速率)工作时,检测器应尽可能接近样品,因为这将带来最佳的灵敏度(图2)。
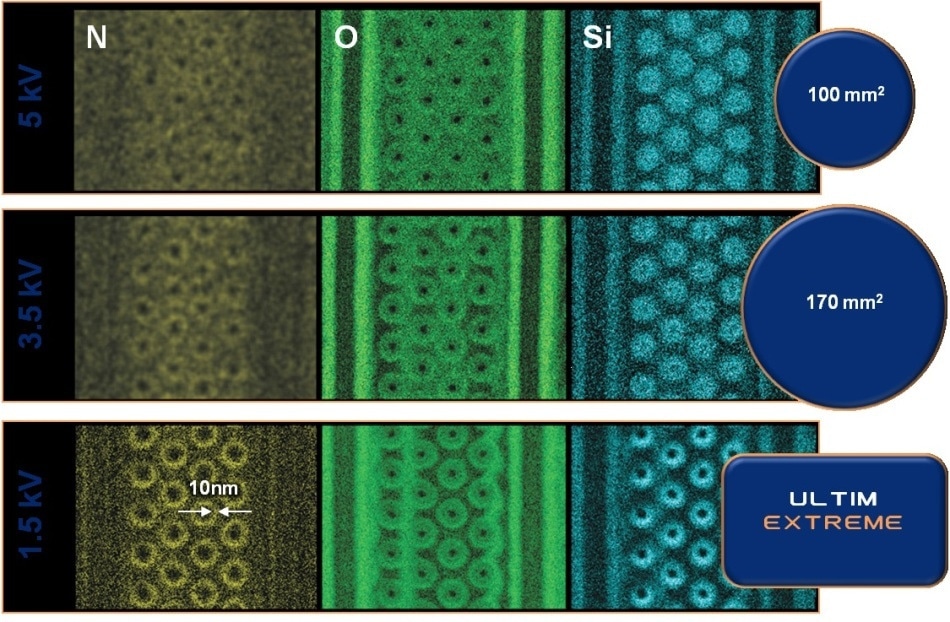
图2。EDS maps for N, O, and Si collected from a NAND flash memory device withUltim100毫米的最大检测器2and 170 mm2传感器区域和Ultim极端。
为了改善空间分辨率,由于Boersch效应,还必须最小化入射光束的电流。为此,该实验是用大约160 pa的入射电子束电流进行的。这给出了5 kV时Ultim MAX 100的输入计数率为1,600 CP,样品检测器距离为7 mm。在这些条件下,EDS数据收集了一个小时。
在5 kV的能量下,EDS地图可用于区分样品中的关键结构,例如氧化物和硅区域,钨单词线(未显示这些地图)。氧图显示了地图中“孔”周围的微弱结构,并且在氮图中也可以看到微弱的结构。
将电子能量降低到3.5 kV意味着更多的结构变得可见。在氧气图中,很明显,在5 kV地图中“孔”周围有分离的环。这些环与硅图中看到的环相对应,氮图中的环结构的存在表明这些环中的每一个都有一个复杂的分层结构。
Factor for Improving Spatial Resolution in Elemental Mapping
This demonstrates that low energy is the most important factor in improving the spatial resolution in elemental mapping. Improving instrument sensitivity towards X-rays of very low energies is possible by removing the X-ray window, which often absorbs 100% of sub kV X-rays.最后的极端具有在极短的分析距离上进行的无窗设计,以优化增强的空间分辨率的灵敏度。
使用与上述相同的条件,但在4.5 mm工作距离和1.5 kV能量的情况下,计数速率为5,200 cps。这种增强的计数率意味着扫描样品仅需30分钟。在1.5 kV的情况下,更多细节在EDS地图中可见,例如设备充电陷阱中明确定义的氮气环。在氧图中也可以观察到高度特异性的表面特征,例如在样品制备过程中发生的离子铣削变化的伪影。
At the very low energy of 1.5 kV the X-ray lines usually used for silicon or tungsten cannot be used. Instead lower energy lines such as LI (0.092 keV) for silicon and N5N6 (0.210 keV) for tungsten can be used. The windowless design of the Ultim Extreme means that these lines can be collected at efficiencies above 80% meaning that accurate elemental maps can still be constructed (图3)。
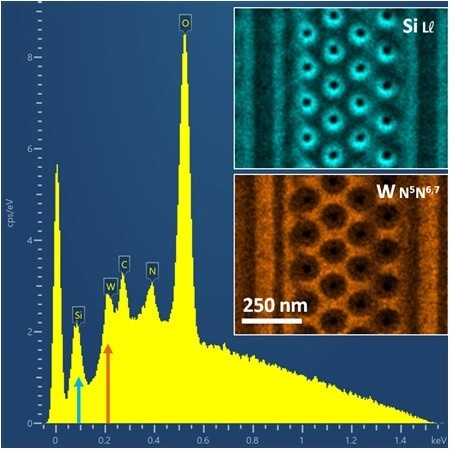
图3。1.5 kV EDS光谱显示Si LL(0.092 KEV)和W N5N6的低能X射线线,7(0.210 KEV)。插入使用这两条X射线线显示元素映射。
对数据采集同样重要的是数据处理。AZTEC trumap可用于实时删除任何背景辐射和反应峰重叠。这允许绘制精确的元素图,而这些图没有光谱伪影(图4)。
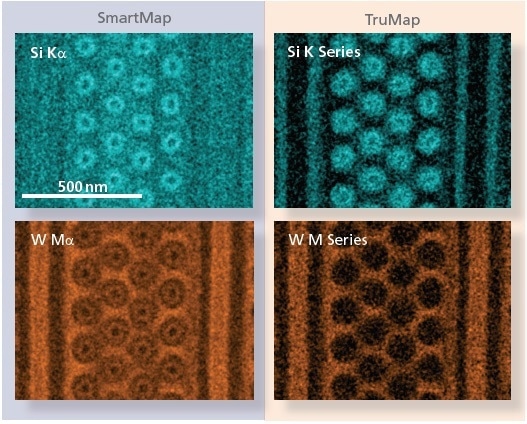
图4。使用窗口积分映射处理以3.5 kV收集的Si和W地图阿兹台克trumap。
在2.5 kV和5 kV硅之间的电子能量和钨之间,可以使用其K和M线分析,分别为1.74 keV和1.77 keV,并且这些线显示强烈的重叠。这种重叠意味着,当观察到具有窗口积分(SmartMap)硅和钨结构的Si K时。
trumap可用于解决此问题,因为它只能显示真实的硅数,因此可以在样品中进行真正的硅分布。
Conclusion
提高一个灵敏度X射线检测器by reducing the sensor-sample distance and/or sensor size, or by removing the window, makes it possible to collect low-energy X-rays at high counts; allowing elemental maps to be collected at resolutions of less than 20 nm, even for light elements.

该信息已从牛津仪器纳米分析提供的材料中采购,审查和改编。亚博网站下载
有关此消息来源的更多信息,请访问牛津仪器纳米分析。