超临界流体(SCF)的环保性质,例如超临界二氧化碳(SCCO)2)has led to the exploration of their use in a range of materials applications. Recently, a number of research groups, including one at Liverpool University, have used the unique physical characteristics of scCO2(和其他流体)为了在无机催化剂支持,生物材料和金属泡沫等区域的潜在应用中生产明确的纳米结构。亚博网站下载 高内相乳液(HIPES)使用乳液模板,一种用于生产多孔材料的多功能方法,在英国达勒姆大学(University of Eun Unike)在英国达勒姆大学(U亚博网站下载niversity of Eun Unike),已开发出改进的技术,用于通过聚合水(W/O)高内相乳液生产交联的聚苯乙烯材料(臀部)。所得的材料或“ Polyhi亚博网站下载pes”具有明确的多孔结构,它们是原始乳液的骨骼复制品。反向方法也是可能的。油含水(O/W)乳房的聚合提供了直接途径,通向一系列多孔亲水材料,包括生物相容性水凝胶。亚博网站下载但是,一个缺点是O/W hipe技术非常溶剂密集型,因为油相量的分数通常大于75%。同样,聚合后可能很难从毛孔中去除有机模板相。 Use of Supercritical Fluids to Produce HIPEs在利物浦大学,我们使用超临界流体克服了这些问题。我们已经开发了一种在没有任何有机溶剂的情况下通过直接聚合高内相CO来产生亲水性多芽的方法2- 水乳液(C/W HIPES),图1.使用此新过程,去除模板相很简单,因为CO2降压后恢复到气态状态。该方法已用于制备孔尺寸少量左右的交联聚丙烯酰胺和聚丙烯酰胺(羟基丙烯酸酯)材料。亚博网站下载该大学的未来目标之一是将此方法扩展到在纳米尺度上具有结构控制的材料的准备。亚博网站下载该大学还正在调查使用CO中使用变化的技术2density to ‘fine tune’ structure. The complete absence of any organic solvents, during both production and purification, may make this method attractive for producing biocomposite materials.
|
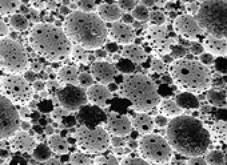
图1。由丙烯酰胺和N,N-甲基双烯酰胺合成的模板C/W hipe合成。近似图像尺寸220x220µm,平均孔径为3.9µm,总孔隙量为3.9厘米3/g. No organic solvents were used in the preparation, only water and CO2。 |
使用超临界流体铸造纳米级铸造Wakayama and colleagues at the Toyota Central R&D Laboratories, Japan, have developed another approach to the preparation of porous materials. Nanoscale casting using supercritical fluids (NC-SCF) takes advantage of several of the important physical properties associated with SCFs. For example, nanoporous silica can be prepared by dissolving silica precursors (e.g. TEOS) in scCO2在将前体连接到活化的碳模具之前。然后除去活化的碳,并涂有铂或其他材料的样品。亚博网站下载日本人发现,他们不仅可以复制宏观形状,例如纤维,而且可以在纳米尺度上复制多孔结构。在此过程中使用超临界流体的关键优势也许是粘度异常低和表面张力的不存在。这意味着在去除溶剂后,即使复杂的纳米结构也可以通过常规液体溶剂难以实现。 光刻
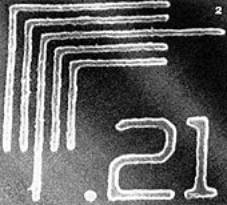
Another process that can benefit from low solvent viscosity is lithography. Supercritical fluids tend to have much lower viscosities than liquid solvents. At Cornell University USA, Ober has developed diblock co-polymer resists for 193 nm wavelength lithography using scCO2作为发展的溶剂。使用这种方法,可以实现低至200 nm的光刻分辨率,结果图2部分是块共聚物所表现出的界面隔离行为的部分。康奈尔队认为SCCO2由于缺乏表面张力,开发可能在高纵横比特征的制造中起关键作用。
|
图2。使用SCCO开发的193nm波长光刻图像的电子图像2。 |
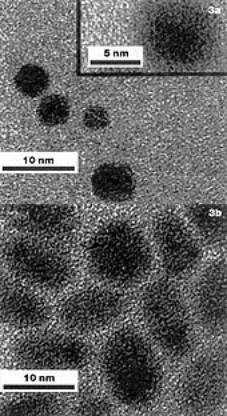
Ober的研究重点是使用超临界CO的图像开发2。实际上,CO的粘度2液态也很低。它具有极低的表面张力和表面能,即使是许多氟化合物,均具有显着的润湿性能。使用这一事实,美国NSF环境响应溶剂和过程中的Carbonell和Desimone已开发出用于直接从液体CO中固定在硅晶片上的自旋涂层的技术2这两种技术的结合可能会导致一个全新的光刻过程,该过程在涂层或开发步骤中不使用任何有机或水性溶剂。 金属纳米颗粒yabo214Given the enormous level of interest in the field of metal nanoparticles, it is perhaps not surprising that supercritical fluid solvents have been explored in this context. The production and processing of nanoparticles is an area in which fine control over solvent properties may offer distinct advantages. For example, Schiffrin and co-workers at Liverpool University have shown that the variable density associated with SCFs may be exploited in the size fractionation of functionalised metal nanoparticles. SCF溶剂中纳米颗粒的实际生产提供了诸如快速溶剂分离,加速反yabo214应速率(由于较高的扩散率)以及将颗粒原位沉积在多孔材料中的可能性,从而利用SCF相的独特性能。亚博网站下载但是,传统方法的纳米颗粒生产和加工方法的一个问题是,它们并不总是可以直接转移。例如,发现不容易分散在SCCO中yabo2142由于这种溶剂表现出非常低的范德华力和极化性。 美国德克萨斯大学的约翰斯顿和科格尔通过在SCCO中通过逮捕的降水量生产氟化合物金属纳米簇来解决了这个问题。2, figures 3a and 3b. The production and processing of metal nanoparticles capped with fluorinated ligands (e.g. 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorodecanethiol) could prove important in applications such as memory storage in which a low dielectric constant coating material may help to insulate the active charge storing devices.
|
图3。SCCO中可溶性有机金属前体亚博网站下载制备的材料的TEM图像2。((a) Iridium nanocrystals coated with C6F13C2H4sh和(b)涂有c的铂纳米晶体6F13C2H4sh。 |
超临界液的未来SCF solvents show great potential for the creation of nanostructures. As recognised for many years in the field of aerogels, surface tension and capillary forces can be highly destructive at the nanoscale. Also, complex supramolecular structures are typically formed in solution, and the self-assembly process is invariably influenced by solvent variables such as density, dielectric constant and polarisability. All of these variables can be fine-tuned in compressible SCF solvents, and the control of molecular self-organisation is likely to be one of the new frontiers for this technology. |